pKa Prediction by Graph-Convolutional Neural Network
Purpose of MolGpKa
Fast and accurate prediction of the pKa values of small molecules is important in the drug discovery process since the ionization state of a drug has significant influence on its activity and ADME-Tox properties. MolGpKa is a web server for pKa prediction using graph-convolutional neural network model. The model works by learning pKa related chemical patterns automatically and building reliable predictors with learned features.
Molecular Graph and Graph Convolutional Neural Network
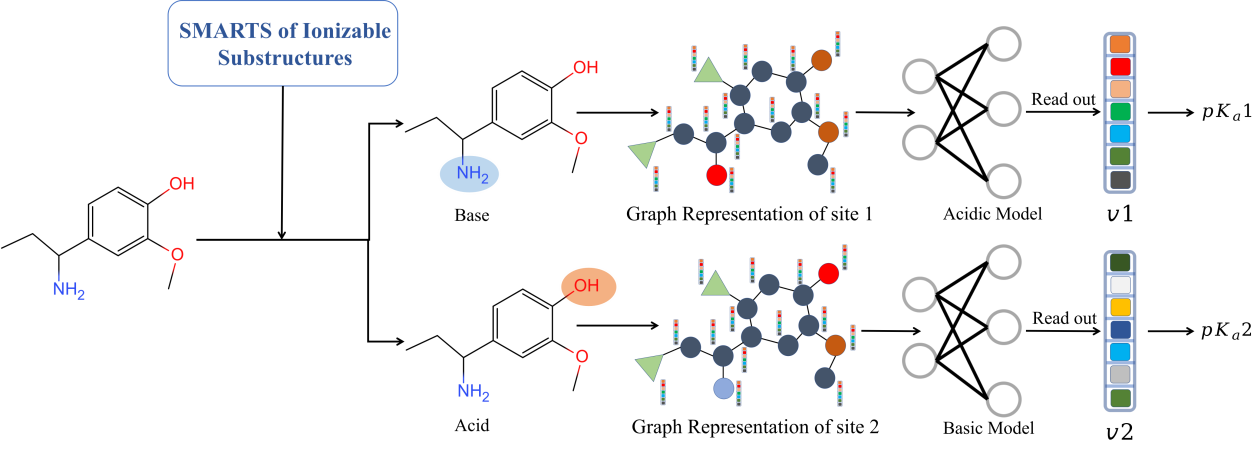
A molecule is composed of atoms connected by bonds. We can treat the atoms and the bonds as nodes and edges of a graph respectively. A molecular graph can be represented as a node features matrix X and an adjacency matrix A. The node features matrix X describes property of each atom, including atom type, atom hybrid state, atom degree and whether it is the ionization center. The adjacency matrix A describes how the atoms are connected in the molecule.
The graph convolutional neural network includes two phases: (i) message passing phase (node convolution), which encodes information of each atom and its neighbors to build an embedded representation Z of the molecule with convolutional layers; (ii) readout phase, which uses the output of the message passing phase to predict pKa with fully connected layers.
Workflow of MolGpKa
MolGpka takes three steps to predict pKa of a molecule. In the first step, the input structure is processed by RDKit, including removing small fragments, neutralizing charges and adding hydrogens. In the second step, ionizable sites are identified by substructure matching. In the third step, the atom feature matrix and the adjacency matrix are built and used as the molecular graph input for pKa prediction by the graph neural network.
Citing MolGpKa
If this service is useful to you, please cite:
Contact
If you have any question about MolGpKa, please contact:
Changge Ji
Chicago.ji@gmail.com